Forex options trading: everything you should know

As we know from general Forex trading theory, the value of one currency is measured against the value of another. This value is constantly changing due to economic, financial, political, and other factors. In the “offline” world, these changes can affect importers who prefer their home country’s currency to be weak, as well as exporters who are better off with the opposite. At the same time, these currency value fluctuations are a key for traders to make a profit when it comes to online Forex trading.
Both importers, exporters, and online financial market players use options and Forex futures to protect themselves against unfavorable currency fluctuations. Forex futures give them the right to buy or sell currency at a specific price on a future date. Sounds pretty good, right? Then for what exactly are Forex options?
These financial derivatives give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell currency at a specific price (strike price) on a specific date in the future (expiry date).
Forex options and their Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are popular among traders for a variety of reasons. Firstly, they have a limited downside risk because they can only lose the premium they paid to purchase the options, but they have unlimited upside potential.
FX options trading is used by some traders to hedge open positions in the Forex “cash market”. In contrast to a futures market, the cash market (also known as a spot market) allows for the immediate settlement of commodity and security transactions. Traders also enjoy Forex options trading because it allows them to trade and profit from market predictions based on economic, political, or other financial news.
Forex options trading is complex and has many moving parts, making it challenging to determine their value. Risks include interest rate differentials (IRD), market volatility, the time horizon for expiration, and the current price of the currency pair, so make sure to dive into Technical and Fundamental analysis to boost your market understanding or use Social trading to automatically copy market professionals.
Key terms of options trading

No matter if you decide to trade traditional options or their CFDs (we’ll talk about them very soon), these terms below are crucial to understanding the market:
- Strike price – also known as “exercise price” – the predetermined price level at which the option contract will be exercised;
- Spot price – current market price for underlying option asset (currency, commodity, index on others);
- Time Value of an option – the amount a trader is ready to pay for an option above its intrinsic value, reflecting the hope that the option’s value increases before expiration thanks to a favorable change in the underlying asset’s price;
- The Intrinsic value of an option – the positive difference between the strike price and underlying spot price;
- The Extrinsic value of an option – the negative difference between the strike price and the underlying spot price;
- A premium of an option – the total amount that traders and investors pay for an option, compounded by two major components: its intrinsic value (amount of money you’d get by exercising an option immediately) and time value (monetarized hope that an option will eventually have value due to a significant change in the underlying asset’s market price).
Major types of options for Forex trading
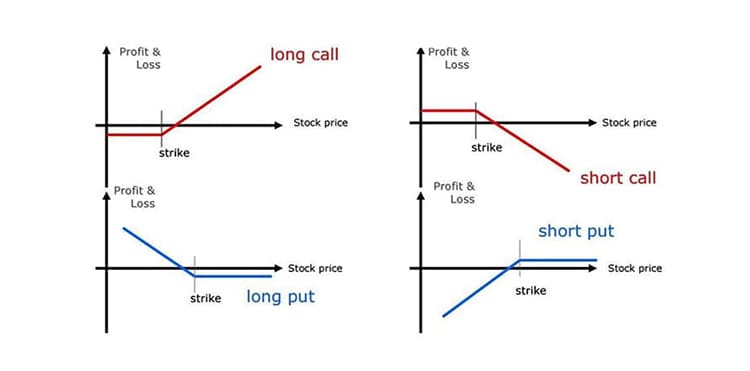
For retail Forex traders, there are primarily two types of options. Both types of trades involve short-term trades of a currency pair with an emphasis on the pair’s future interest rates.
Put or Call traditional vanilla options
As we mentioned above, a traditional, or vanilla, options contract gives the trader the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at the agreed-upon price and execution date. In the case of Forex, the trade will still involve being long one currency pair and short another. In essence, the buyer will state how much they want to buy, the price they want to pay, and the expiration date. A seller will then respond with the trade’s quoted premium. Traditional options may have expiration dates in either American or European styles (European options may be exercised only on the option’s expiration date, i.e. at a single pre-determined point in time. In comparison, an American option can be exercised at any time before the expiration date). The options will expire worthlessly if the current exchange rate causes them to be out of money (OTM).
Single Payment option trading (SPOT)
A SPOT option’s contract structure is more flexible than a traditional option’s. This strategy is an all-or-nothing trade, and also may be referred to as binary or digital options. The buyer will present a scenario like “EUR/USD will break 1.3000 in 12 days.” They will be given premium quotes that represent a payout based on the likelihood of the event occurring. If this event occurs, the buyer will profit. If it does not happen, the buyer forfeits the premium they paid. Usually, SPOT contracts are more expensive than traditional options contracts and can also be written to pay out if they reach a specific point, several specific points, or do not reach a specific point at all.
CFD trading of Forex options

As we said in the introduction, an option in the traditional trading market is a contract in which the seller grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying instrument such as a stock, commodity, index, Forex pair, or other assets with a fixed price that the asset must reach before the expiry date.
In the CFDs market, rather than actually owning any options, the buyer/seller can speculate on the price difference between the option’s opening and closing. The position is closed at the last available rate when the option CFD expires.
Options CFDs are built with the same components as traditional ones, including Put or Call matter, underlying assets for an option, strike price, and expiration date.
Trading with options CFDs generally offers greater exposure than trading other instruments as it is available for leveraged trading with trusted regulated brokers, allowing traders to open bigger positions with less capital.
Differences between traditional and CFD options

Options CFDs are very similar to traditional options, but there are a few important differences. Trading options CFDs involve speculating on the future price (strike price) of underlying assets like stocks, indices, or any other.
To make our comparison more precise, let’s take as an example option CFDs provided by Plus500 – a reliable CFD broker under FCA regulation and more than a decade of market history.
Plus500’s option CFDs are all cash-settled (actual physical delivery of an actual asset never occurs). The most notable distinction between traditional and CFDs options here is when an option CFD expires, cash is credited or debited to the trader’s balance, based on the difference between the opening and closing price, whereas traditional options holders have the right to exercise the trade.
Or, let’s look at this in another way. When we talk about traditional options, we assume that:
- As a traditional Call or Put option Seller, you are exposed to significant loss potential;
- Usually, quite a lot of money is required to get into the market;
- Traditional options offer the possibility of future ownership of an asset;
- The trader can pay a commission based on the size of the position;
At the same time, trading of options CFDs with Plus500:
- Plus500 offers risk management tools to its clients such as Stop Loss, Limit Stop, Guaranteed Stop, and others;
- Trading on a CFD account has a set “Unit Amount” per instrument, which is the smallest size of trade or number of contracts/shares, etc. required to open a position;
- You can only lose as much as your account balance when trading CFDs;
- Plus500 doesn’t charge Commissions on options CFDs;
- As CFDs options are leveraged, you can open a larger position with the same capital.
82% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
What influences the price of options CFDs?
In the traditional market, the value of options is determined by factors such as the underlying asset price, strike price, market volatility, and time to expiration. Traders can then analyze these variables and incorporate their findings into trading strategies with the goal of maximizing profits.
CFDs options use underlying instrument factors such as the it’s market price and strike price. They are also influenced by market movements similar to traditional options. The main goal of trading CFDs options is to speculate on the price of the underlying instrument and determine whether it will rise or fall before the expiration date. The trader then has the “option” to close the position for a profit or loss (depending on the market movement).
Let’s break down these major factors:
The market price of the underlying asset
CFD Options track the market movements of the underlying asset for an Option as market movements are heavily influenced by the underlying instrument’s supply and demand. This, in turn, influences the behavior of a Call or Put option. When the price rises, the value of Call options tends to rise as well, meaning that Call options CFD buyers may benefit from the asset’s rising price, but may also suffer a loss if the price falls. Put options, on the other hand, typically trend downward in value when the underlying instrument price rises; thus, in the case of trading Put options CFDs buyers may benefit from a falling market price.
If the speculation is incorrect and the price moves in the opposite direction, the option may lose value and the position will be closed at a loss.
The strike price of an option
The strike price is arguably the most important variable in determining the value of an option as it is the underlying instrument’s price at which the option expires. Strike prices are predetermined and fixed prior to the start of the contract. The option’s value is determined by the price difference between the current and the Strike Price. options CFDs are also available at various strike prices, but they cannot be exercised.
Options Market Volatility
It is, probably, one of the most important market concepts for traders as price changes are the source of trading profit. The impact of volatility on an option’s price is determined by a metric known as Historical Volatility (also known as Statistical Volatility) examining past price movements of the underlying asset over a specified time period.
During this time period, experienced traders will use different option pricing models to forecast future volatility, including calculating interest rates, the time value in the traditional market, and other factors. When there is volatility, options tend to gain more value together with when the underlying instrument is volatile, option CFD prices react.
Implied volatility is a key metric that allows traders to forecast future volatility. Traders assess the likelihood of future price changes by examining the volatility behavior of the asset’s price in the current time frame.
Time Value on an option
Time Value has two variables (assuming the market price and volatility levels have not changed): time until expiration and how close the strike price is to the underlying instrument price. The longer the market has until the expiry date, the more time it has to hit the strike price.
Options hedging in the Forex trading
To hedge trading risks in the Forex market with different assets, traders usually use a common set of instruments: futures, forwards, and options. The latter is known to be the right, but not obligation to buy the asset, so it provides lucrative flexibility in your trading decisions.
There are two types of options: call options to buy assets and put options to sell assets.
Usually, traders manage their deals according to the following rules: in order to insure an asset against depreciation, you need to buy a put option or sell a call option. If an increase in the price of the asset is undesirable, then the put option should be sold, or the call option is bought.
Safe Forex options trading with VPN

The best option for remaining anonymous and completely confident in your security while trading traditional Forex options, their CFDs, or any other financial instruments is to use Top VPN services for Forex trading. You can use a VPN to buy and sell assets, trade CFDs, Cryptocurrencies, options, futures, and other derivatives, track market trends, and remain incognito to other users and the government.
Furthermore, in cases of direct network connection via public Wi-Fi, VPN services’ strong encryption algorithms and data transfer protocols will protect your personal and important trading account information from fraudsters.
Best Forex brokers for trading of options and their CFDs
Options traded in the Forex market differ from those traded in other markets in that they allow traders to trade without physical delivery of the asset. Forex options traders can select prices and expiration dates that are appropriate for their hedging or active trading strategy. Unlike futures traders, who must fulfill the terms of the contract at expiration, options traders do not have that obligation but only the right to deal with a certain asset.
Trading options CFDs boarders your market exposure by supporting leveraged trading. Also, you can use risk management tools available on advanced brokers’ trading platforms to mitigate the risk of potential losses. With all of this in mind, if you want to speculate on market value changes or hedge your exposure, CFD options may be a worthy option to consider.
In addition to being highly regulated and trustworthy, two brokers reviewed and recommended for options trading by our experts offer a variety of trading tools and other financial instruments to positively differentiate their offerings from the competition. When trading with these brokers, you can employ a broad variety of trading tactics and diversify your portfolio, adding not only different assets but also their derivatives. These brokers offer a variety of retail account types, user-friendly trading interfaces, and Forex demo accounts to practice your trading strategies in the real market environment.
Plus500 options CFDs trading
Leverage – 5:1 ($100 to gain $500-worth of capital), the number of available options CFDs – 350+
Plus500 provides CFDs on multiple derivatives and instruments, including options CFDs for currency pairs, commodities, stocks, indices, and others (more than 2000 in total), as well as a demo account that is the exact replica of real one, trading guide, and all the tools you need to trade efficiently and safely.
Plus500 clients can trade on the web terminal for PCs and laptops, and also have access to the mobile app for Android and iOS. As we said before, there are two types of accounts: real and demo. The second will give new brokers an ideal opportunity to practice, and increase their trading competence by gaining important knowledge in real market conditions while remaining completely risk-free.
Plus500 is licensed by the UK Financial Services Authority, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, and the New Zealand Financial Markets Authority. It is also a regulated financial services provider in South Africa licensed by the Financial Conduct Authority.
82% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
AvaTrade options trading
The number of available options – 40+ currency and any combination of Call and Put options in one single account.
AvaTrade, in addition to a variety of financial instruments such as currency pairs, commodities, Cryptocurrencies, and indices, provides Vanilla options trading, giving traders the right to buy or sell a certain amount of an instrument at a certain price at a predetermined time. When trading Vanilla options, a trader can control not only the instrument and the amount he trades, but also when and at what price.
AvaTrade offers CFDs on currency pairs, leading stock indices such as the S&P500, commodities (gold, metals, energy, agricultural products), and shares of leading global companies, including pre-IPO exchange-traded ETFs, in addition to derivatives such as options. When trading CFD contracts, traders can use the leverage of up to 1:200.
MT4, MT5, Proprietary, AvaSocial, AvaTradeGo, AvaOptions, and WebTrader are among the trading platforms available. If you don’t want to be tied to a computer, AvaTrade has a mobile app.
AvaTrade is regulated by a number of institutions, including IIROC, BVIFSC, FSCA, ASIC, ADGM, FSA, and FFAJ. It also provides platforms and features like AvaSocial and AvaTrade Protection. The first platform is the Copy Trading platform, which allows you to copy the deals of successful traders that you select and profit in the same way they do. The second compensates you for losing trades at the end of the month in exchange for a hedging cost to use this tool.
Forex Options and their CFDs trading - FAQ