Maximize your Forex trading with these 5 powerful Technical indicators
While there are many factors that influence currency price movements, technical analysis provides traders with a structured approach to understanding market behavior. By analyzing historical price data and trends, traders can identify potential opportunities and risks.
Technical indicators play a vital role in this process. These tools help traders assess market momentum, trends, volatility, and possible reversal points, guiding them to make more confident trading decisions. In this article, we’ll explore the top 5 technical analysis indicators every Forex trader should know:
1. Moving Averages (MA)
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
3. Bollinger Bands
4. Fibonacci Retracement
5. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Moving Averages (MA) Technical analysis indicator

Moving Averages (MAs) are one of the most widely used technical indicators in Forex trading, helping traders smooth out price data and identify trends over a specific period. They calculate the average price of a currency pair over a certain number of periods, updating as new data becomes available. There are two main types of moving averages:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This is the straightforward average of the closing prices over a specific period. For example, a 50-day SMA is the average of the past 50 days’ closing prices.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Unlike the SMA, the EMA gives more weight to recent price data, making it more responsive to recent price movements. This makes the EMA particularly useful in fast-moving markets like Forex.
Moving averages are primarily used to identify the direction of a trend:
Uptrend: If the price is consistently above the moving average, it signals an upward trend.
Downtrend: If the price is consistently below the moving average, it indicates a downward trend.
Sideways/Range Market: If the price hovers around the moving average, it may suggest the market is in a range or lacks clear direction.
Moving averages can also act as dynamic support and resistance levels, with prices often bouncing off these lines during trends.
Common trading strategies using Moving Averages
One of the most popular strategies that incorporate moving averages is the Moving Average Crossover:
- Golden Cross: This occurs when a short-term moving average (e.g., 50-day SMA) crosses above a long-term moving average (e.g., 200-day SMA). It’s considered a bullish signal, suggesting a potential buy opportunity.
- Death Cross: Conversely, this happens when a short-term moving average crosses below a long-term moving average, signaling a potential sell opportunity.
These crossover strategies are simple yet effective for traders looking to capitalize on new trends, as they can highlight shifts in market momentum.
By using moving averages, traders can gain a clearer picture of the market’s direction and filter out short-term fluctuations that may be confusing.
See how these indicators work with the example of Apple Inc. stocks
Relative Strength Index (RSI) Technical analysis indicator

The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. Developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr., the RSI ranges from 0 to 100 and is typically used to identify whether a currency pair is overbought or oversold.
The RSI calculates momentum by comparing the magnitude of recent gains to recent losses over a specified period, usually 14 days. The formula for RSI is:
RSI = 100 – 100:(1+RS),
where RS (Relative Strength) is the average of N days’ up closes divided by the average of N days’ down closes. The result is a value that reflects the strength of price movements, helping traders assess whether a currency pair may be due for a correction.
The RSI is often interpreted using the following thresholds:
- Overbought condition: An RSI above 70 indicates that a currency pair may be overbought, suggesting that prices have risen too quickly and may soon decline.
- Oversold condition: An RSI below 30 signals that a currency pair may be oversold, indicating that prices have fallen too sharply and could be due for a rebound.
These levels serve as warning signals for traders to be cautious about entering new positions in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Spotting potential reversals with RSI
Traders often use the RSI to identify potential reversal points in the market. Here are a few common strategies:
- Divergence: When the price of a currency pair makes a new high or low that is not confirmed by the RSI, it signals a potential reversal. For example, if the price reaches a new high while the RSI fails to do so, it suggests weakening momentum and may indicate a trend reversal.
- RSI Crosses Thresholds: Traders may also look for opportunities when the RSI crosses above 30 (oversold) or below 70 (overbought). For instance, an RSI crossing back above 30 may signal a buying opportunity, while a drop below 70 could indicate a potential sell signal.
- Centerline Cross: An RSI crossing the 50 level can also indicate a shift in momentum. A move above 50 suggests bullish momentum, while a move below indicates bearish momentum.
By integrating the RSI into their trading strategies, traders can enhance their ability to spot potential price reversals, making it a valuable tool in their technical analysis toolkit.
See how these indicators work on the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJI) chart
Bollinger Bands Technical analysis indicator

Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s. They consist of three lines that are plotted on a price chart: the middle band, the upper band, and the lower band. The middle band is typically a 20-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), while the upper and lower bands are calculated by adding and subtracting a certain number of standard deviations (usually 2) from the middle band.
Bollinger Bands are primarily used to measure market volatility. When the market is volatile, the bands widen, reflecting greater price fluctuations. Conversely, when the market is stable or less volatile, the bands contract. This dynamic nature of the bands allows traders to gauge the prevailing market conditions effectively.
- Widening bands: Indicates increased volatility, often seen during strong trends or market events.
- Narrowing bands: Suggests decreased volatility, often occurring before significant price movements.
The concept of price “bouncing” between the bands is a key principle in Bollinger Bands analysis. Prices tend to oscillate within the upper and lower bands, often touching or approaching them before reversing direction.
- Upper Band: This represents a potential resistance level; when prices approach or touch this band, it may indicate an overbought condition.
- Lower Band: Acts as a potential support level; when prices approach or touch this band, it may suggest an oversold condition.
Traders often look for opportunities when the price reaches these bands, anticipating a reversal or correction.
Anticipating breakout opportunities with Bollinger Bands
1. Breakouts: When the price breaks above the upper band, it may signal a strong bullish momentum, while a break below the lower band can indicate bearish momentum. Traders often use these breakouts as entry signals, provided there is confirmation from other indicators.
2. Squeeze: A “squeeze” occurs when the bands contract, signaling a period of low volatility and potentially foreshadowing a significant price movement. Traders watch for breakouts in either direction after a squeeze, using it as a cue to enter trades.
3. Trend confirmation: If prices consistently stay above the middle band during an uptrend, it reinforces the bullish sentiment. Conversely, if prices stay below the middle band in a downtrend, it reinforces bearish sentiment.
By effectively using Bollinger Bands, traders can not only assess market volatility but also identify potential reversal and breakout opportunities, making them a valuable addition to any technical analysis strategy.
Look at NVDA stock analysis: key indicators, trading strategies, and market predictions
Fibonacci Retracement Technical analysis indicator
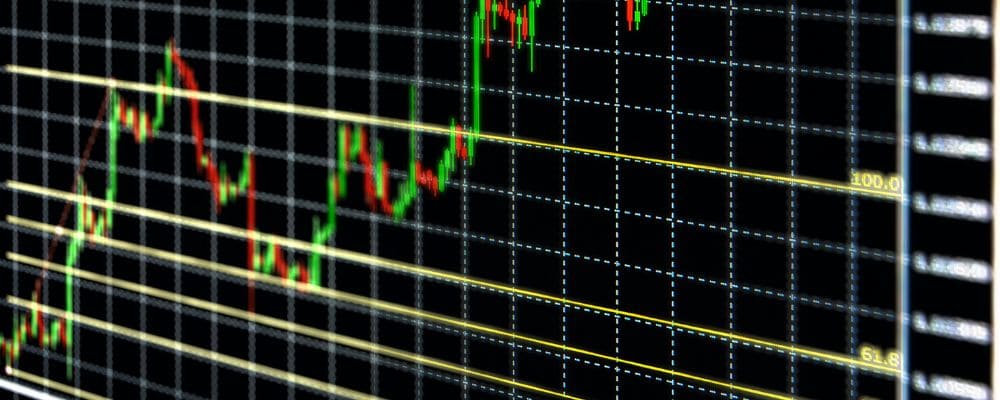
Fibonacci retracement is a popular technical analysis tool used to identify potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. This sequence, discovered by the Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci, consists of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones (e.g., 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, etc.). The key ratios derived from this sequence, commonly used in trading, include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%. These ratios help traders predict possible reversal levels during retracements.
The primary Fibonacci levels of interest are calculated by taking the vertical distance between a significant high and low point in the price chart and applying the Fibonacci ratios:
- 23.6%: Minor retracement level
- 38.2%: Often seen as a critical reversal level
- 50%: Not a Fibonacci ratio but widely recognized as a significant psychological level
- 61.8%: Considered the most important Fibonacci level, often called the “golden ratio”
- 100%: Indicates the original price level before the retracement
Traders use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify potential support and resistance levels during price corrections. When the price retraces a portion of the previous move, it often bounces off these Fibonacci levels:
- Support level: In an uptrend, Fibonacci levels can serve as support where traders expect prices to rebound after a pullback.
- Resistance level: In a downtrend, Fibonacci levels may act as resistance, where traders anticipate a price reversal following an upward retracement.
By plotting these levels on a chart, traders can visually assess where price action is likely to encounter support or resistance.
Planning Entry and Exit points with Fibonacci retracement levels
Fibonacci retracement levels play a significant role in planning entry and exit points for trades:
1. Entry points: Traders often look to enter long positions at Fibonacci support levels during uptrends or short positions at resistance levels during downtrends. A bounce from a significant Fibonacci level can serve as a strong signal to enter a trade.
2. Stop-loss placement: Traders may set stop-loss orders just below the Fibonacci support levels for long positions or just above resistance levels for short positions to minimize potential losses.
3. Profit targets: Fibonacci levels can also help traders identify potential profit-taking levels. For example, if a trader enters a long position at a Fibonacci support level, they might set a target near the next Fibonacci resistance level.
By incorporating Fibonacci retracement into their trading strategies, traders can enhance their ability to identify critical price levels, plan trades more effectively, and manage risk in dynamic Forex markets.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) Technical analysis indicator
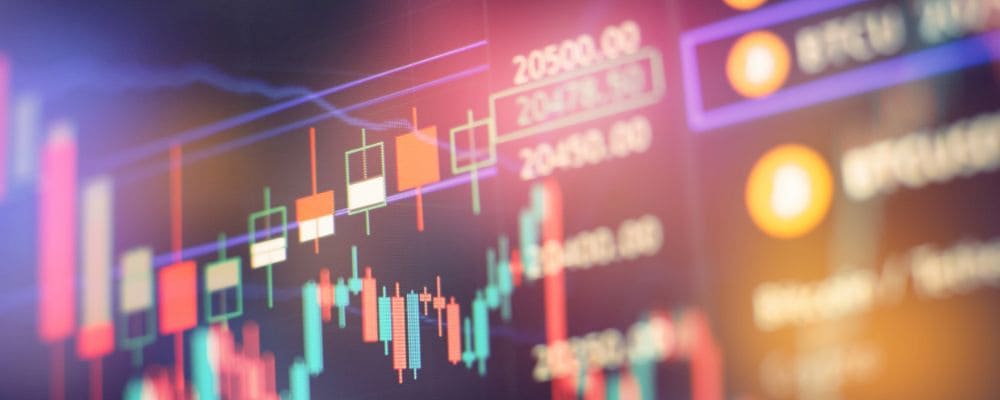
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a versatile and widely used technical analysis indicator that helps traders assess the strength and direction of a trend. Developed by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s, the MACD consists of three main components:
- MACD line: This is the difference between two Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs)—typically the 12-day EMA and the 26-day EMA. The MACD line reflects the momentum of price movements and is plotted on the chart.
MACD Line = {12-day EMA} – {26-day EMA}
- Signal line: This is a 9-day EMA of the MACD line. The signal line helps smooth out the MACD line and provides a basis for generating buy and sell signals.
- Histogram: The histogram represents the difference between the MACD line and the signal line. It is plotted as bars on the chart, illustrating the momentum’s strength. When the MACD line is above the signal line, the histogram is positive, indicating bullish momentum. Conversely, when the MACD line is below the signal line, the histogram is negative, indicating bearish momentum.
The MACD indicator is useful for identifying both trend direction and momentum:
- Trend direction: When the MACD line is above the zero line, it indicates a bullish trend, while a MACD line below the zero line suggests a bearish trend. The position of the MACD line relative to the signal line further confirms the trend’s strength.
- Momentum: The MACD histogram indicates the strength of the momentum. A growing histogram suggests increasing momentum, while a shrinking histogram indicates weakening momentum. Traders often look for significant changes in the histogram to assess potential trend reversals or continuations.
MACD Crossover trading strategy
The MACD crossover strategy is one of the most popular methods used by traders to generate buy and sell signals:
1. Bullish crossover: This occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line. This crossover is interpreted as a potential buy signal, suggesting that upward momentum is increasing.
2. Bearish crossover: Conversely, when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, it generates a sell signal, indicating that downward momentum is gaining strength.
Traders often combine MACD crossovers with other indicators or price action signals for confirmation before entering a trade. Additionally, the MACD can help identify overbought or oversold conditions when used alongside levels like 70 and 30.
Overall, the MACD is a powerful indicator that provides valuable insights into market momentum and trend direction. By employing the MACD crossover strategy, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve their chances.
Using Technical analysis with trusted Forex brokers
When employing Technical analysis tools like the ones discussed, having a reliable broker is crucial for executing trades effectively. Brokers mentioned below provide robust trading platforms and resources that enhance the trading experience.
AvaTrade
AvaTrade, known for its user-friendly platform and educational resources, offers a range of trading tools, including advanced charting features that integrate seamlessly with technical indicators like Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD. Traders can leverage AvaTrade’s comprehensive market analysis and access to multiple asset classes, allowing for diversified trading strategies.
OANDA
OANDA is renowned for its transparent pricing and reliable execution speed. It provides a wealth of historical data, making it easier for traders to backtest their strategies using Fibonacci retracement levels and Bollinger Bands. OANDA’s advanced trading platform supports various technical indicators, ensuring that traders have the tools they need to make informed decisions.
Exness
Exness stands out for its flexible leverage options and tight spreads, making it an attractive choice for both new and experienced traders. The platform allows for real-time analysis and quick execution of trades based on signals from indicators like the MACD and RSI. Exness also offers an economic calendar and market insights, helping traders stay updated on potential market-moving events.
NAGA Markets
NAGA Markets combines social trading with advanced trading technology, enabling traders to learn from experienced peers and follow successful trading strategies. With NAGA’s platform, users can easily incorporate technical analysis tools, such as Fibonacci retracement and Bollinger Bands, into their trading routines. The social trading feature allows users to see how top traders utilize these indicators, providing additional insights into effective trading practices.
By trading with these reputable brokers, Forex traders can access advanced tools and resources that complement their technical analysis efforts. Each of these brokers offers unique features that can enhance your trading strategy, whether you’re focusing on trend identification with Moving Averages, spotting reversals with RSI, or planning entries and exits using Fibonacci levels. Choosing the right broker can make a significant difference in your trading performance and overall success in the Forex market.
Related articles:
Top 5 Technical analysis indicators every Forex trader should know - FAQ